Fibre Contact Angle and Wetting
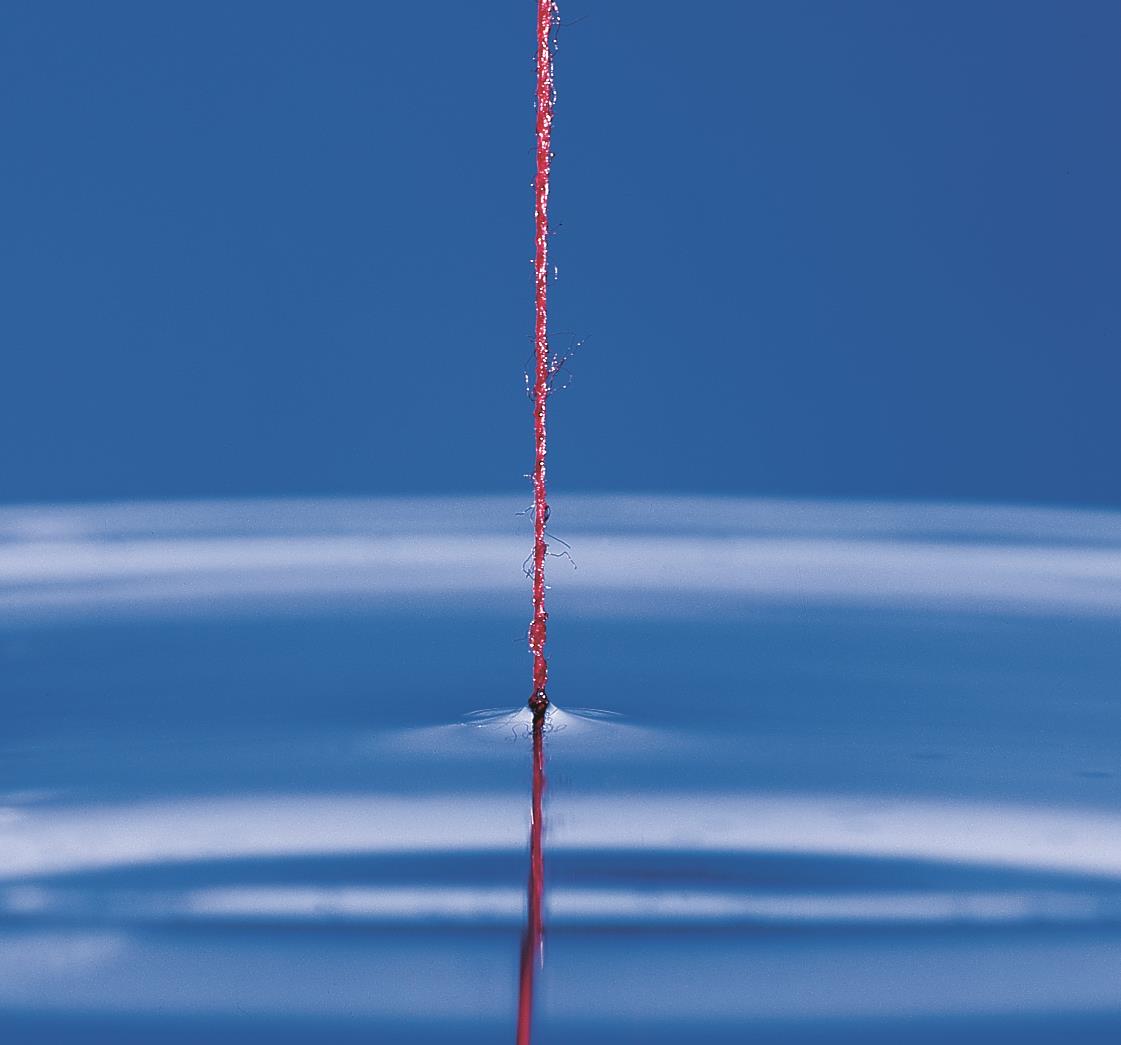 Measurements of fibre wetting has applications in a wide range of industries. These include composite materials using carbon fibres, textiles and the paper industry. An example of an application of fibre wetting measurement is the textile industry where studying the effect of different coatings can allow the water repellant performance of different garments to be predicted.
Measurements of fibre wetting has applications in a wide range of industries. These include composite materials using carbon fibres, textiles and the paper industry. An example of an application of fibre wetting measurement is the textile industry where studying the effect of different coatings can allow the water repellant performance of different garments to be predicted.
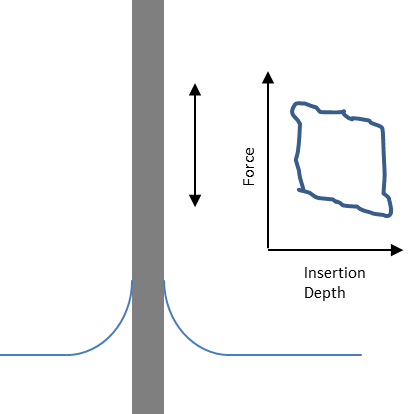
LPD Lab Services is able to measure fibre contact angles using force tensionmetry with a Dataphysics Dynamic Contact Angle Tensiometer (DCAT21). Fibre samples are attached to a special sample holder and slowly lowered into a liquid test sample. The tensionmeter then measures the advancing and receding contact angle as the fibre sample is slowly raised and lowered into the liquid. Fibre dynanmic contact angle measurements can be made over several measurement cycles allowing mean values to be calculated and variability assessed. The sensitivity of the equipment is such that it enables single fibres with diameters down to 5um to be measured.
 The physical behaviour can also be understood looking in the SEM at fibre surface roughness as this affects microscopic wetting and localised contact angles. Chemical interactions can be understood by surface chemical analysis of bundles of fibres. An example is the quantitative measurement of size pick up by XPS in composite materials in carbon fibre reinforced plastics: Size treatments are important for load transfer between fibre reinforcement and matrix polymers.
The physical behaviour can also be understood looking in the SEM at fibre surface roughness as this affects microscopic wetting and localised contact angles. Chemical interactions can be understood by surface chemical analysis of bundles of fibres. An example is the quantitative measurement of size pick up by XPS in composite materials in carbon fibre reinforced plastics: Size treatments are important for load transfer between fibre reinforcement and matrix polymers.