Nickel Plating Assessment, Coating Integrity and Failure
 Nickel plating is typically used to protect materials like steel from corrosion and provide more aesthetic appearances even on plastics. LPD Lab Services has a metallographic facility and the metallurgy expertise to assess the integrity of nickel plating and advise on improvements to the electrolytic or electroless coating process or substrate cleaning and preparation. Typical assessment techniques include light optical microscopy and SEM/EDX. The coating can be evaluated top-down or in cross section.
Nickel plating is typically used to protect materials like steel from corrosion and provide more aesthetic appearances even on plastics. LPD Lab Services has a metallographic facility and the metallurgy expertise to assess the integrity of nickel plating and advise on improvements to the electrolytic or electroless coating process or substrate cleaning and preparation. Typical assessment techniques include light optical microscopy and SEM/EDX. The coating can be evaluated top-down or in cross section.
Typical nickel plating defects that can occur are:
- Pits.
- Porosity.
- Inclusions.
- Gaps or holidays.
- Insufficient thickness.
- Loss of adhesion – peeling, delamination and blisters.
- Cracking after plating from hydrogen cracking.
- Cracking from mechanical work and damage like deep drawing.
- Dull and hazy deposits in plating.
- Oxidation of the plating.
- Substrate contamination affecting seed layer in electroless nickel.
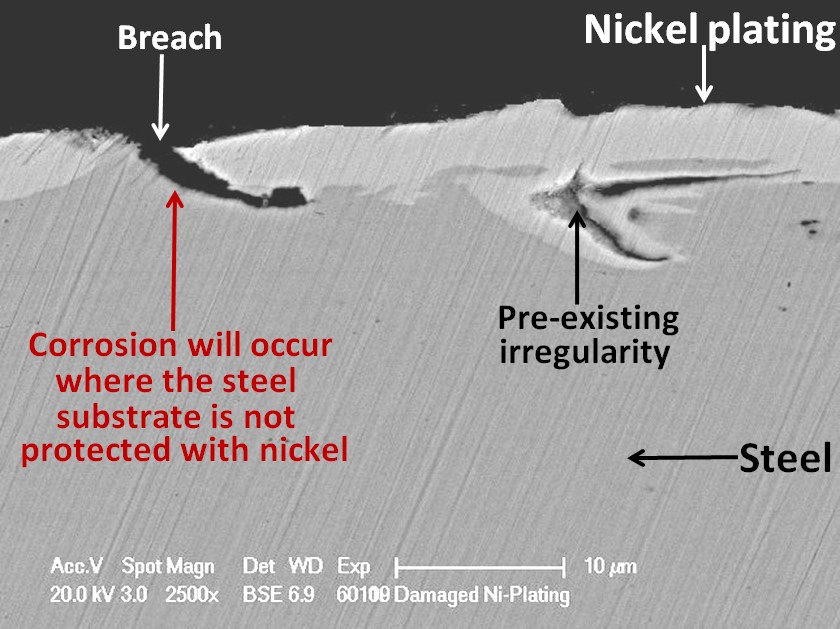
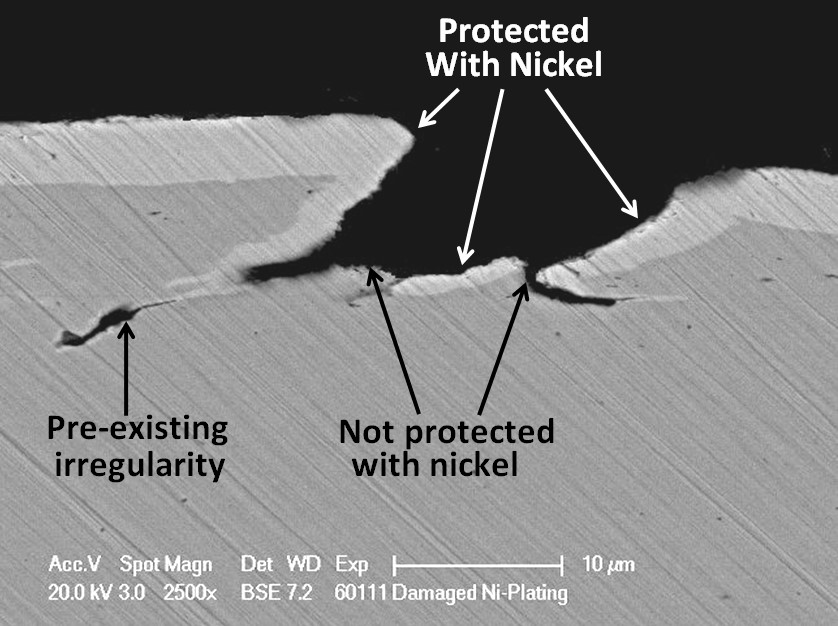 Iron is a cheap and versatile metal, but it has very low corrosion resistance. To make iron and its various alloys durable, it is plated with a thin layer of metal which has very good corrosion resistance. Nickel has superior chemical and corrosion resistance along with great wear resistance, making it an obvious choice for plating carbon steel engineering components. This is a very cheap alternative to fabricating the same component entirely out of nickel, which is a very expensive metal. Bright nickel coatings also find application where aesthetics is important.
Iron is a cheap and versatile metal, but it has very low corrosion resistance. To make iron and its various alloys durable, it is plated with a thin layer of metal which has very good corrosion resistance. Nickel has superior chemical and corrosion resistance along with great wear resistance, making it an obvious choice for plating carbon steel engineering components. This is a very cheap alternative to fabricating the same component entirely out of nickel, which is a very expensive metal. Bright nickel coatings also find application where aesthetics is important.
Unfortunately, nickel is a nobler metal than iron. This means that when nickel is in contact with steel in moisture, a galvanic cell will be created in which the steel will corrode preferentially to the nickel. It is, therefore, very important that the nickel plating should be completely intact, not having any defects where the steel substrate is be exposed otherwise pitting corrosion can result. Not all defects are due to the plating process. Some can arise from surface irregularities in the substrate material.