Metallurgy Failure Analysis Consultancy
Metallurgy is a term that includes a wide range of practices related to the extraction of metals from their ores, refining the crude metals, producing alloys, their shaping and the manipulation of their properties. Metallography is a branch of metallurgy that is concerned with the examination and characterisation of the structure of metals and alloys. At LPD Lab Services analysis, interpretation and consultancy of the metals data is carried out or overseen by the laboratory’s Senior Metallurgist Danie Els generating metallurgical failure analysis reports.

Metallography
The mechanical properties of alloys are determined by both the chemical composition and the microstructure. Metallography aims to identify microstructural phases, estimating the volume fraction of each phase, assessing the grain size, and discovering defects or irregularities.
To assess the microstructure of an alloy, a cross-section is systematically prepared by rough grinding, fine grinding, polishing and etching. Mounting in a resin is used for the preparation of small sections. A non-destructive approach can be adopted by replicating the surface microstructure using acetate sheet or a bespoke medium.
Examination is performed using binocular microscopes (5x to 25x magnification), light optical microscope (50x to 1000x magnification), or scanning electron microscopes SEM / EDX (50x to more than 10000x magnification).
Metallography is routinely used in quality control and is indispensable in conducting failure examinations and reverse engineering. Together with hardness testing and microhardness testing, metallography can indicate the effectiveness of thermal-mechanical treatment or welding processes and the accuracy of heat treatment processes.
Fractography
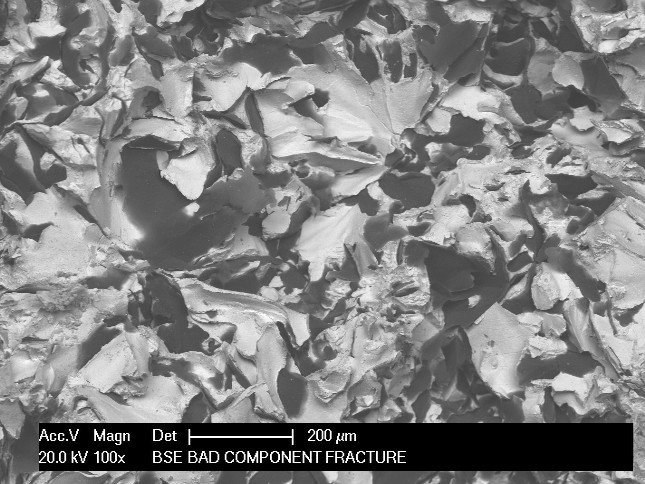

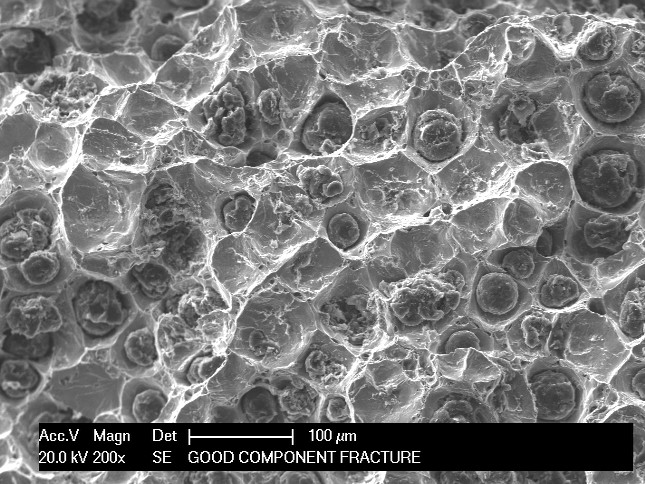
Fractography is the study of characteristic features on fracture surfaces to determine the nature of the fracture and to identify the fracture initiation point. It is applied to metals and non-metallic materials. Fractographic analysis is the first step in analysing the root cause of a failure. It begins with visual examination, followed by low power magnification (typically using a binocular microscope).
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can also be applied to aid fractography at a finer scale and characterise flaws like stress concentrators, inclusions or porosity. EDX in the SEM allows the composition of any inclusions to be determined at initiation sites for example.
LPD Lab Services applies metallography and fractography along with other advanced analytical techniques such as Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) and 3D X-ray imaging to assist in failure and root cause analysis as well as product and process development.

Typical Applications of Physical Metallurgy
- Engine component failure analysis and internal corrosion.
- Bearing failure investigation.
- Tool failure and wood drill metallurgical failure investigation.
- Weld assessment and failure investigation, weld inclusions and determination of size of heat affected zone HAZ.
- Detecting Residual Stress and SCC testing in Copper Alloys – Brass, Bronze and Cupronickel.
- Cutting Tool Failure and Jigsaw Blade Metallurgical Failure Investigation.
- Checking for grades of cast iron - spheroidal, grey and white cast irons.
- LECO carbon and sulphur IR analysis in metals and alloys like steels, nickel and cobalt superalloys, brass bronze and copper alloys.
- Cleaning and degreasing of metals.
- Microstructure and grain size assessment.
- Corrosion and high temperature oxidation of metals.
- Heat treatment and surface treatment of metal components including nitride hard coatings on steel assessed by microhardness measurements.
- Powder metallurgy and failure investigation including sintering and green cracking problems.
- Surface preparation, chemical etching, electrochemical and pickling processes.
- Anodising of aluminium alloys and castings for painting or adhesive bonding.
- Hardness and friction and wear.
- Alloy and metal component analysis.
- Landfill gas engine and power generation system failure investigations.
- Plating blistering and uniformity using cross-sectional analysis.
- Confirmation of raw material structure and composition.
- Parts comparison for engine production and alternative supplier evaluation.
- Root-cause for overload failure in cast metal components.
- Metal fragment and foreign particle identification and analysis.
- Assessment of structural changes in heat treated steel.
- Impurity analysis in various metals using ICP-OES.
- Steam boiler tube failure examination including water wall, superheater and reheater.
- Coatings and layer measurement.
Example Metallurgy, Failure Analysis and Consultancy report
Example Cutting Tool Failure and Jigsaw Blade Metallurgical Failure Investigation report
Example Metallurgical Examination of a Failed Automotive Helical Suspension Spring report