Anion and Cation - Ion Chromatography - IC Analysis
Ion chromatography (IC) is a separation technique used to analyse aqueous solutions for ionic species for anions, cations and weak organic acids.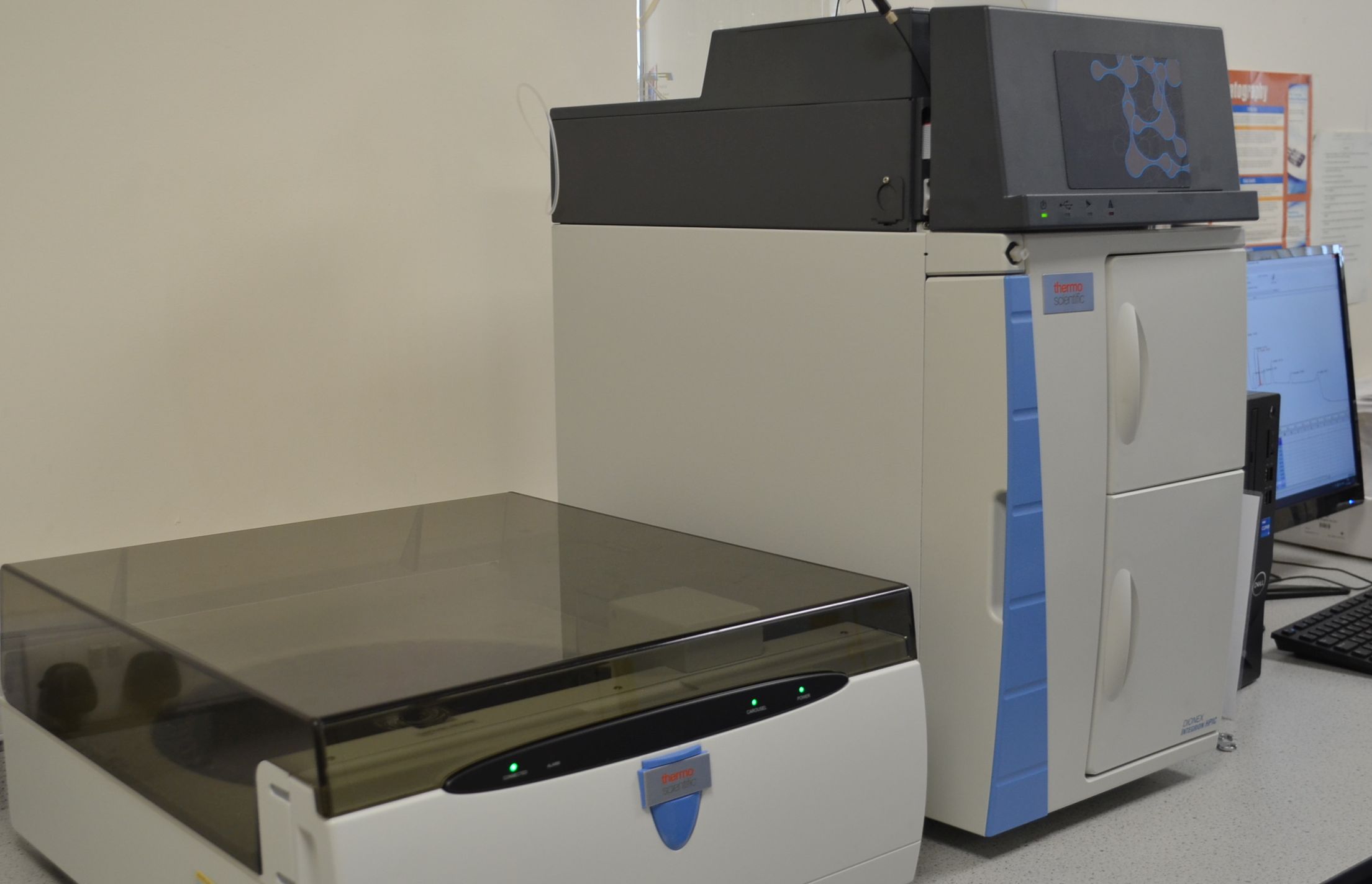
The IC analysis methods available at LPD Lab Services allows the detection, identification and quantification of concentrations of major anions such as:
- Fluoride (F)
- Chloride (Cl)
- Bromide (Br)
- Nitrate (NO3)
- Nitrite (NO2)
- Phosphate (PO4)
- Sulphate (SO4)
IC can also be used for the following cations:
- Sodium (Na)
- Potassium (K)
- Lithium (Li)
- Calcium (Ca)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Ammonia ions (NH4)
The laboratory has the capability to detect, identify and measure numerous weak organic acid WOA species.
The laboratory has a UKAS accredited method to measure water soluble anions.
Applications of Anion, Cation and WOA Chromatography
The Anions and Cations can be analysed over a large dynamic range of concentrations on a wide range of samples including:-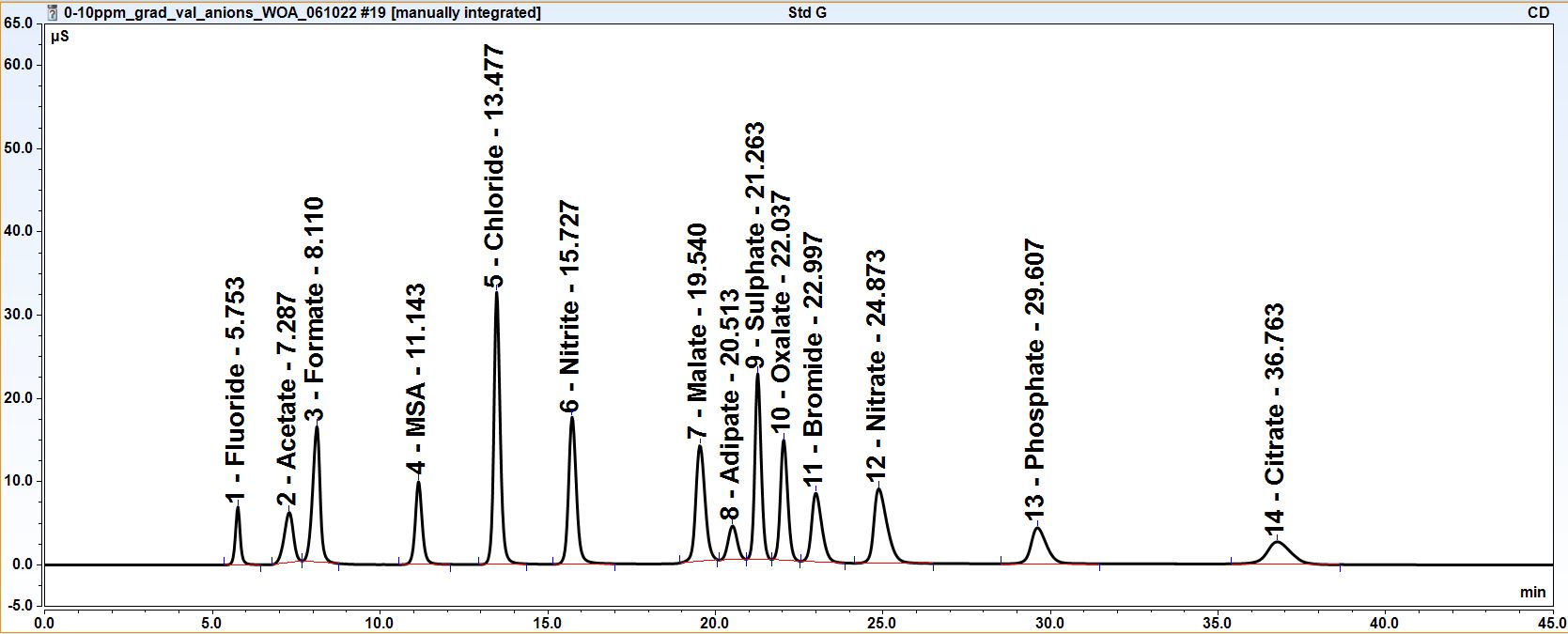
- Drinking, towns and demineralised waters.
- Ionic contamination analysis of PCBs.
- Ground water and Rainwater.
- Wastewater or Effluents.
- Cooling and recirculating water.
- Analysis of ions in chemical products, beverages, foods, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals.
- Analysis of soluble anions and cations on environmental monitoring filters.
- Analysis of soluble / leachable anions and cations from solid samples such as medical devices and polymers.
- Traces of exposure to salt water or sea spray (chloride) promoting corrosion as rust on steel, under or on paint coatings, on aluminium or on various metal surfaces.
- Checks for aggressive ions that might promote corrosion on material surfaces or leached from the bulk like phenolic foam pipe insulation and WOA that promote ants nest corrosion of copper.
- Determination of anions and cations in bulk materials or from washed or rinsed surfaces.
- Raw material or chemical Quality specification checks.
- Identification of WOA generated from Microbiologically Induced Corrosion MIC in glycol treated recirculated water systems.
- Screening of aqueous inks for potentially corrosive species.
- Degradation and consumption of polymer stabilisers like aryl phosphates and fire retardants.
- Checking for stress corrosion cracking promoting ammonia species in brass plumbing fittings.
Methods can also be performed on a diverse range of sample matrices allowing accurate reliable results.
The IC technique also allows detection of rarer anions such as Chlorite, Chlorate, Bromate and Acetate.
Weak Organic Acids
Ion Chromatography can be used to analyse a variety of weak organic acids WOA. These are organic compounds that have acidic properties but do not fully dissociate in water (which make them weak acids). While there are many organic acids, not all of them are sensitive enough to be detected by ion chromatography. Below is a list of common organic acids that are easily detected by ion chromatography, this list is not definitive and it may be possible to analyse for less common weak organic acids as well.
- Acetic acid
- Adipic acid
- Benzoic acid
- Butyric acid
- Caproic acid
- Carbonic acid
- Citric acid
- Glutaric acid
- Formic acid
- Lactic acid
- Malic acid
- Methane sulphonic acid
- Oxalic acid
- Propionic acid
- Tartaric acid
Anion, Cation and Weak Organic Acid Chromatography Detection Limits
The limit of detection that can be obtained in most cases will be dependent on the anions or cations being analysed for, however typical detection limits of 0.1 ppm down to parts per billion levels are achievable.
Ion Chromatography Instrumentation
For the analysis of anions and weak organic acids LPD uses a dedicated Dionex Integrion HPIC system. For the analysis of cations LPD uses a Dionex DX320 IC system. Each system uses a dedicated auto-sampler allowing large numbers of samples to be analysed efficiently.
Please contact us if you do not see the specific activity you require, we may still be able to help you.