Potentiostat Electrochemical Testing
 Electrochemical testing using a potentiostat including Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy EIS is an excellent way to quantify the corrosion and to investigate details not visible otherwise. Electrochemical testing is very sensitive to surface events. It determines electrochemical characteristics of a system, measures corrosion rate of material and passivity / pitting behaviour. Electrochemical data is normally presented in the form of graphs which are easy to compare for the purpose of e.g. materials compatibility (galvanic corrosion prevention), corrosion resistance / rates in different environments, coatings performance.
Electrochemical testing using a potentiostat including Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy EIS is an excellent way to quantify the corrosion and to investigate details not visible otherwise. Electrochemical testing is very sensitive to surface events. It determines electrochemical characteristics of a system, measures corrosion rate of material and passivity / pitting behaviour. Electrochemical data is normally presented in the form of graphs which are easy to compare for the purpose of e.g. materials compatibility (galvanic corrosion prevention), corrosion resistance / rates in different environments, coatings performance.
 Potentiostat Electrochemical Testing Applications
Potentiostat Electrochemical Testing Applications
- Determining the porosity in coatings.
- Detemining the overportential for passivation.
- Determining the effectiveness of anticorrosion inhibitors and impact of water additives.
- Determining electrochemical compatability of materials to assess and prevent galvanic corrosion.
Basic Electrochemical Corrosion Tests
- Open Circuit Potential OCP reflects thermodynamic tendency of the material to participate in the electrochemical corrosion with the electrolyte.
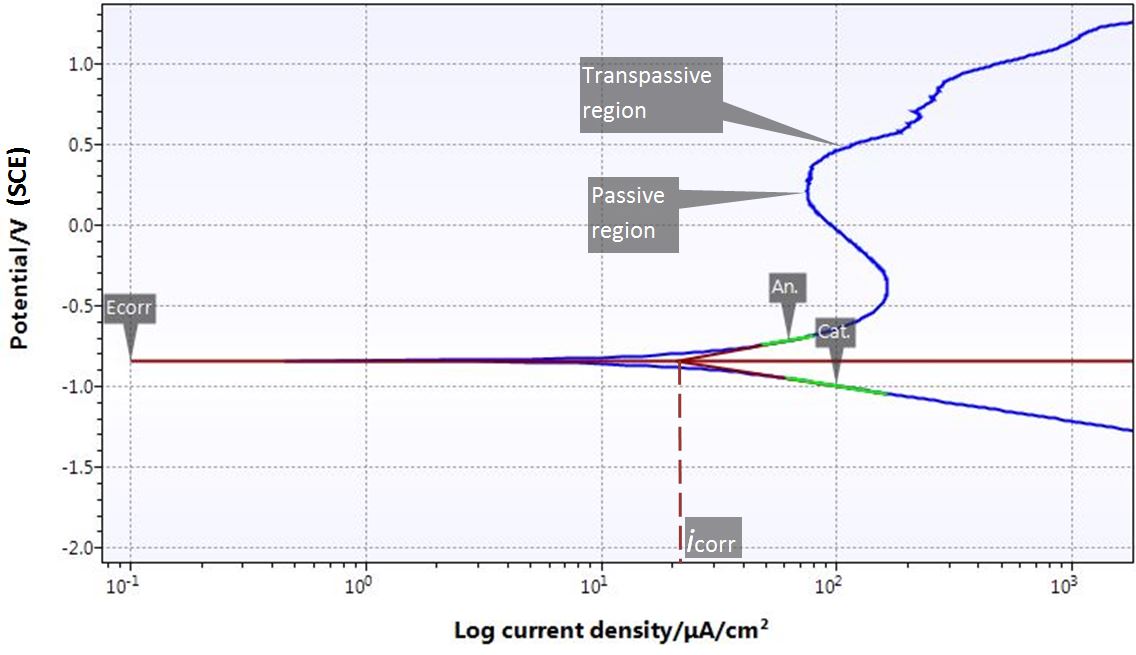
- Tafel Plots to determine corrosion current and corrosion rate.
- Potentiodynamic Polarisation to assess passive and pitting behaviour as well as compare corrosion rates.
- Galvanic corrosion coupling to measure galvanic corrosion rates and potentials of dissimilar metals which can drive corrosion.
- Electrochemical Impedence Spectroscopy EIS study of the performance of protective anti-corrosion coatings.