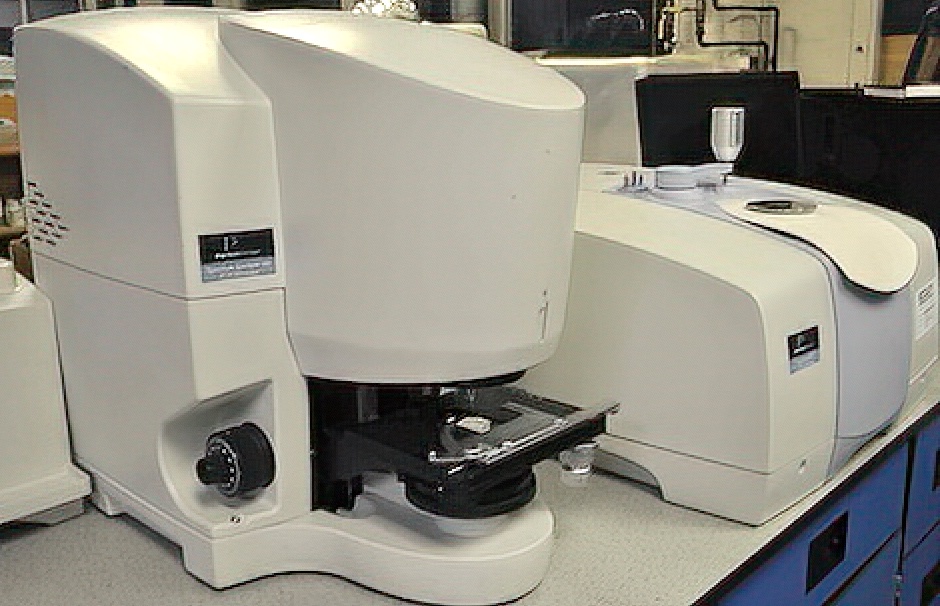
FTIR Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometer and Microscopy
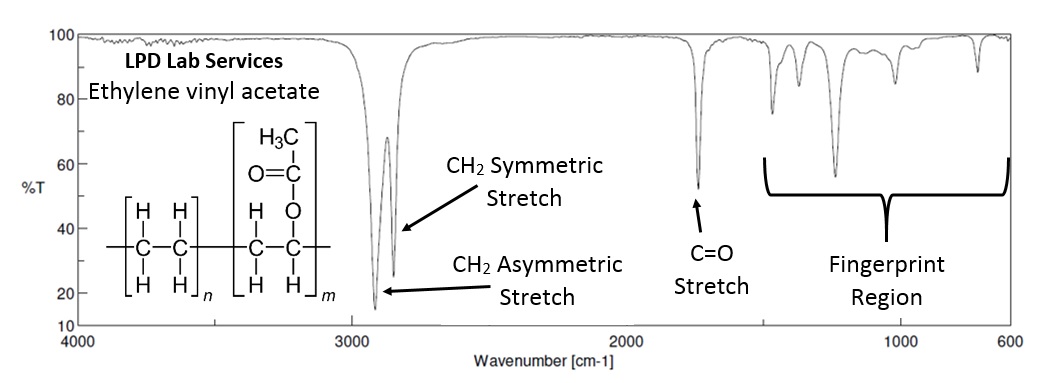
 FTIR Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometry is a sensitive technique particularly for identifying organic chemicals in a whole range of situations including solid, liquid and gas samples. FTIR can also be used to characterise some inorganic compounds. It may be used to identify both pure compounds and simple mixtures.
FTIR Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometry is a sensitive technique particularly for identifying organic chemicals in a whole range of situations including solid, liquid and gas samples. FTIR can also be used to characterise some inorganic compounds. It may be used to identify both pure compounds and simple mixtures.
LPD Lab Services instruments also feature an FTIR Microscope that enables the collection of FTIR spectra of extremely small samples to examine the composition of individual particles and materials. Examples include paints, adhesives, resins, polymers, rubbers, coatings, pharmaceuticals and additives used in food and other consumer goods. It is a particularly useful tool in isolating and characterising organic contamination.
Typical Applications of FTIR and FTIR Microscopy
- Routine qualitative and quantitative FTIR analysis.
- Low volume Quality Control and Pharmacopeia testing.
- Identification of polymers and polymer blends.
- Assessment of changes of polymers and rubbers due to both ageing and environmental degradation like oxidation and hydrolysis.
- Indirect identification of trace organic contaminants on surfaces.
- Thin film analysis of organic coatings and oxide thicknesses on metals such as aluminium.
- Analysis of adhesives, coatings and adhesion promoters or coupling agents.
- Small visible and Microscopic particle chemical analysis by FTIR microscopy.
- Analysis of stains and surface blemishes remnant from cleaning and degreasing processes combined with optical microscopy, SEM / EDX, XPS, SIMS and FTIR microscopy techniques.
 Analysis of resins, composite materials and release films.
Analysis of resins, composite materials and release films.- Solvent extractions of leachables or contaminants, plasticisers, mould release agents and weak boundary layers coupled with XPS surface chemical analysis techniques.
- FTIR identification of rubbers and filled rubbers coupled with pyrolysis GC-MS.
- Determination of degrees of crystallinity in polymers like LDPE and HDPE.
- Comparative chain lengths in organics.
- Extent of thermal, UV or other degradation or depolymerisation of polymers and paint coatings.
- Analysis of a gaseous samples using a gas cell for headspace analysis or environmental monitoring.
- FTIR analysis of unknown solvents, cleaning agents and detergents combined with GC-MS.
 Temperature dependent study of materials using the heated stage accessory.
Temperature dependent study of materials using the heated stage accessory.- Small visible and microscopic particle chemical analysis by FTIR microscopy.
- Contaminants in pharmaceutical API’s, WFI water for injection and blood products.
- Identifying specific fibres and particles in inhalable dust by FTIR microscopy and SEM / EDX.
- FTIR microscopy of microplastics in freshwater, sea water, soil and wastewater with pyrolysis GC-MS.
- Checks for localised antiseptic chemical products and wipes attack of rubbers and plastics in hospitals and the medical device industry.
- Cross-sectional analysis and imaging of different primer, top coat and clearcoat paint layers looking for missing layers, interface contaminants combined with SEM / EDX of filler materials.
- FTIR analysis and reverse engineering of unknown compounds and formulations particularly when combined with GC-MS.
- Evaluation of chemical reaction pathways, rates of reaction and assessment of reaction completion.
- Analysis and characterisation of antimicrobial coatings and polymers by FTIR, pyrolysis GC-MS and XPS.
- Quantitative analysis of ethanol in hand sanitiser using a fixed path length liquid cell.
Application Notes
| Document Title | View |
| Contaminant Particle Identification and Elimination | |
| Determination of Surface Tension and Wettability of Liquid on Solid Surfaces |
Our site experts on FTIR are Aeryn May, Kim Nickson and Mike Ellicott.
Please contact us to discuss how your requirements can be met using this or any of our analytical techniques.