Chemical Analysis Techniques
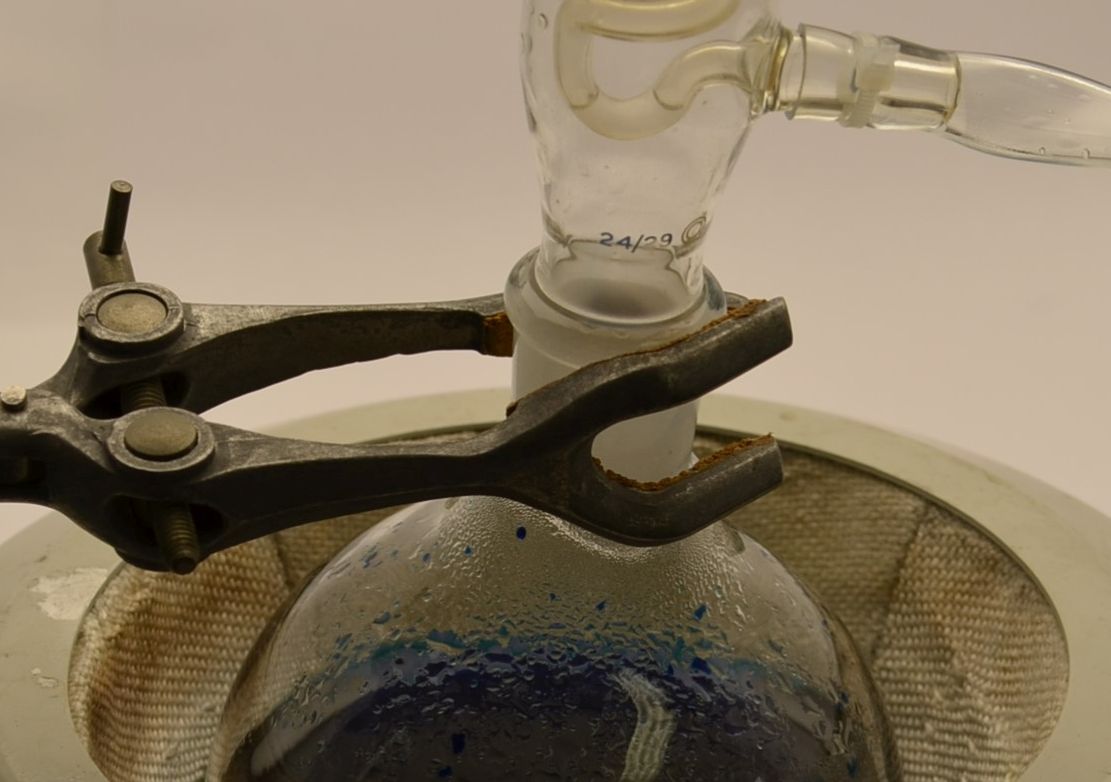
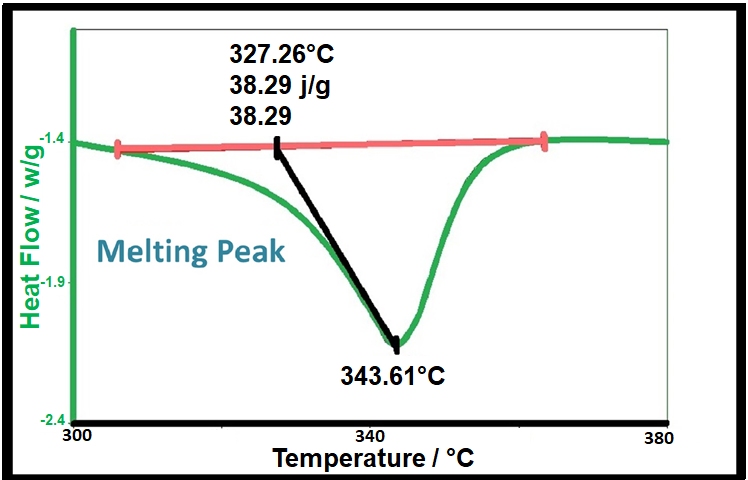
 Chemical analysis covers a wide range of techniques and an even broader range of samples including solids, liquids and gases from raw materials to finished products. Analysis may involve using a particular or combination of techniques and may be related to a specific problem to solve or product of process research and development. At LPD Lab Services our team of dedicated specialist technical staff have access to many chemical analysis and materials analysis techniques and can advise how best to best address customer requirements in a cost effective and reliable way.
Chemical analysis covers a wide range of techniques and an even broader range of samples including solids, liquids and gases from raw materials to finished products. Analysis may involve using a particular or combination of techniques and may be related to a specific problem to solve or product of process research and development. At LPD Lab Services our team of dedicated specialist technical staff have access to many chemical analysis and materials analysis techniques and can advise how best to best address customer requirements in a cost effective and reliable way.
Our Industrial scientist and engineering backgrounds and typical technical expertise mean practical context orientated interpretation of the experimental data is included as a matter of course, giving customers the confidence to act directly upon the results with appropriate support.
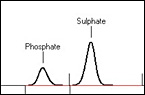
Some of the chemical analytical techniques available at LPD Lab Services are:
Please contact us if you do not see the analytical technique you require, we may still be able to help you.